
- #TASKHOSTW EXE HOW TO#
- #TASKHOSTW EXE DRIVERS#
- #TASKHOSTW EXE FULL#
- #TASKHOSTW EXE PC#
- #TASKHOSTW EXE WINDOWS 8#
If there are any problems, it will show you. You can observe that the System File Checker is scanning the files on the Windows system. In Command Prompt, type sfc/scannow to run SFC. Search command prompt in the search box and then right click the best-matched result to Run as administrator.Ģ. For instance, some users can know whether the taskhostw.exe file is corrupted after the System File Checker checks all the files.ġ. You need first to scan all the system files like the DLL or executable files to ensure there is no corruption among them.
#TASKHOSTW EXE PC#
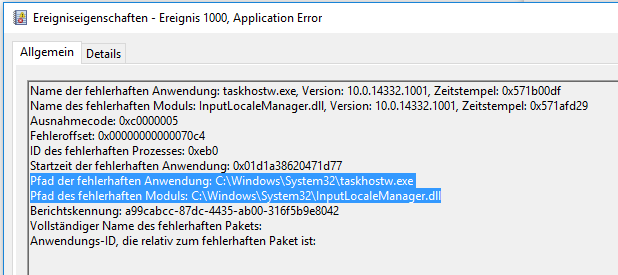
In other cases, if you find the taskhost.exe else instead of the subfolder of C: hard drive, you need to scan your PC for malware or problematic files. If so, you might as well try solutions to solve taskhostw exe high CPU. Or malware or malicious files have pretended to be the taskhostw exe, thus resulting in various problems. Therefore, once you noticed taskhostw.exe high CPU, it means that this file is corrupted. This single file should not have occupied too many resources on your computer. Unfortunately, some users hit upon high usage caused by the taskhostw exe file on Windows 10. While you can also disable this exe file if you find it useless for you.
#TASKHOSTW EXE FULL#
However, it is only when the taskhostw.exe file on your PC causes problems like full disk or high CPU usage that you are advised to block the taskhostw.exe file. Since taskhostw exe is a system file that is crucial to launch Windows services during system boot up, you would better keep this executive file on your PC. Normally, users can find this file in C:\ProgramData-primarily C:\ProgramData\RealtekHD\.
#TASKHOSTW EXE WINDOWS 8#
In some cases, you may see no taskhostw.exe on your system but taskhostex.exe on Windows 8 or taskhost.exe on Windows 7. Simply out, taskhostw exe serves as a host for processes to execute DLL files instead of executable files as itself.
#TASKHOSTW EXE HOW TO#
How to Fix Taskhostw.exe High CPU Usage?Īs a Windows-based system file, taskhostw.exe is used to launch the Windows Services supported by DLLs when your device boots up.This tutorial tries to give you a full guide about the taskhostw EXE on Windows systems. Your PC is freezing due to the problems with the taskhostw exe file. Sometimes, when you open task manager, only to find taskhostw.exe high CPU usage on Windows 10. If the file is stored in your Windows\System32 folder, then you can be fairly certain you are not dealing with a virus.You have no idea what taskhostw.exe is and are wondering whether you can remove it from Windows 10. In Task Manager, right-click Host Process for Windows Tasks and choose the “Open File Location” option. If you’d like to be sure, you can check out Host Process for Windows Tasks’ underlying file location. We’ve seen no reports of viruses that hijack this process. While it’s possible that a virus has replaced the real Host Process for Windows Tasks with an executable of its own, it’s very unlikely. The process itself is an official Windows component. It’s essential for being able to load DLL-based services onto your system and, depending on what you’ve got running, disabling Host Process for Windows Tasks could break any number of things. Windows won’t even let you temporarily end the task. No, you can’t disable Host Process for Windows Tasks. It then loads each of those services, and you’re going to see it consuming a fair bit of CPU during that time. When Windows starts, the Host Process for Windows Tasks scans the Services entries in the Registry and builds a list of DLL-based services that it needs to load. This is also normal behavior and should settle down quickly. You will notice that right after startup, all instances of Host Process for Windows Tasks may look like they’re consuming extra resources–especially the CPU. If you notice that any single instance of Host Process for Windows Tasks continually uses more resources than you think it should, you’ll need to track down which service is attached to that instance and troubleshoot the related service itself. Normally, each service will consume the resources it needs to do its job and then settle back down to a baseline of activity.

Typically, the CPU and memory each instance of Host Process for Windows Tasks just depends on what service the entry is attached to. Why Does It Use So Many Resources at Windows Startup? So, I’m going to assume it’s the service that monitors for when I press any of the media keys on my keyboard (volume, mute, and so on) and delivers the appropriate commands where they need to go.
#TASKHOSTW EXE DRIVERS#
Looking through the details in the lower pane, I’m able to piece together that this service is linked to my audio drivers and also has Registry keys associated keyboard layout.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
